What is a fiber optic cable?
fiber optic cable is a high-speed data transmission medium that uses thin strands of glass or plastic (called **optical fibers) to transmit information as pulses of light. These cables are widely used in telecommunications, internet services, medical equipment, and military applications due to their **high bandwidth, low latency, and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI)
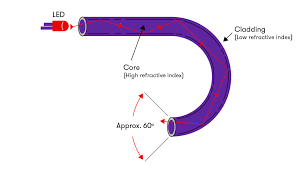
Key Components of a Fiber Optic Cable
1. Core
- The central part where light travels (made of ultra-pure glass or plastic).
- Diameter: *9µm (single-mode), 50µm or 62.5µm (multimode)
2. Cladding
- A layer surrounding the core that reflects light back into the core (lower refractive index)
3.Buffer Coating
- A protective plastic layer that prevents physical damage.
4. Strength Members
- Kevlar or aramid yarn to protect the fiber from tension.
5. Outer Jacket
- A rugged outer layer (PVC, LSZH, etc.) for environmental protection.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
1. Single-Mode Fiber (SMF)*
– *Core size:* ~9µm
– *Light source:* Laser (1310nm, 1550nm)
– *Use case:* Long-distance (100+ km), high-speed (e.g., telecom, ISPs).
2. Multimode Fiber (MMF)*
– *Core size:* 50µm or 62.5µm
– *Light source:* LED/VCSEL (850nm, 1300nm)
– *Use case:* Short-distance (up to 500m), LANs, data centers.
3. Specialty Fibers*
– *Armored Fiber:* Metal-coated for extreme environments.
– *Tactical Fiber:* Military-grade, ruggedized.
– *Bend-Insensitive Fiber (BIF):* Resistant to bending losses.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
✔ *Extremely high bandwidth* (Terabits per second).
✔ *Low signal loss* (<0.2 dB/km in SMF).
✔ *No EMI/RFI interference* (unlike copper cables).
✔ *Secure* (hard to tap without detection).
✔ *Lightweight & thin* compared to copper.
Disadvantages*
✖ *Higher cost* (installation & equipment).
✖ *Fragility* (fibers can break if bent too tightly).
✖ *Complex splicing/termination* (requires precision tools like fusion splicers).
Common Applications*
– *Telecom/Internet* (FTTH, 5G backhaul).
– *Data Centers* (high-speed server connections).
– *Medical* (endoscopy, laser surgery).
– *Military/Aerospace* (secure, lightweight comms).
– *Industrial* (factory automation, sensors).